Table of Contents
Scan a Network/Subnet
Host Discovery
HOST DISCOVERY:
-sL: List Scan - simply list targets to scan, without sending any packets to the target hosts,
useful to generate list of target hosts and dns resolution.
-sn: Ping Scan - disable port scan.
-Pn: Treat all hosts as online -- skip host discovery.
-PS/PA/PU/PY[portlist]: TCP SYN/ACK, UDP or SCTP discovery to given ports.
-PE/PP/PM: ICMP echo, timestamp, and netmask request discovery probes.
-n/-R: Never do DNS resolution/Always resolve.
nmap -sn 192.168.1.1/24 # ping scan
nmap -sn -PS22-25,80,113,1050,8080,35000 192.168.1.1/24 # custom TCP SYN scan
nmap -sn -PU82,9001,9030,9050-9051 192.168.1.1/24 # custom UDP scan
Scan a large public network
-
Identify the IP block:
mtr -brw -y1 target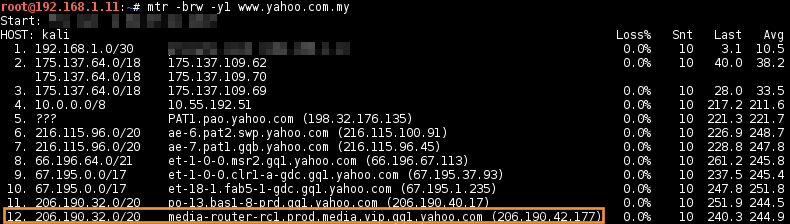
-
Do a ping scan only (
-sn) and write three output formats/results (-oA) to three files:nmap -v -sn target -oA output-
for completed in
-
takes approx. additional
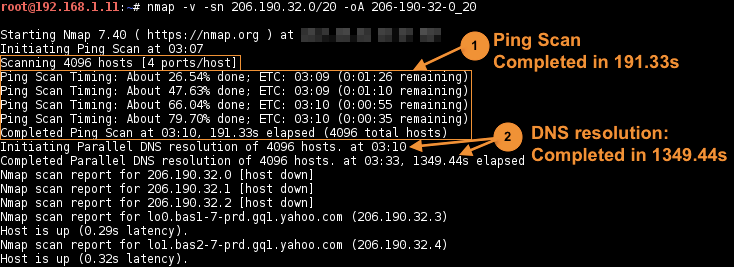
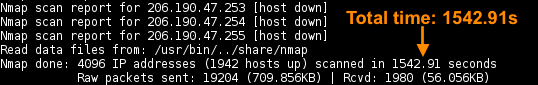
Note: the DNS resolution phase prolonged the total time (
-nto disable DNS resolution): -
-
Ping scan without DNS resolution (
-n):# nmap -v -sn -n target -oA output-
without DNS resolution completed in
-
Total time is , approx of speedup.
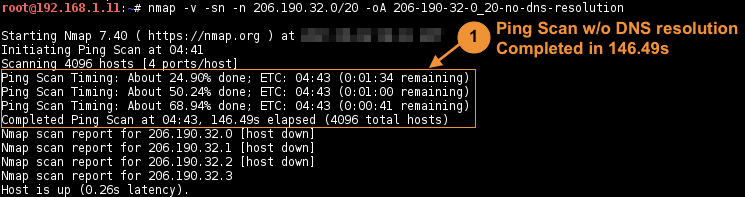
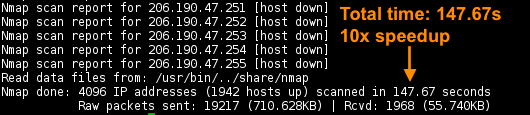
-
Scan a private network: 192.168.1.0/24
-
Do a TCP SYN scan (
-sS) with OS detection (-O) and output results in three major formats (-oA):-v: increase verbosity level -sS: TCP SYN scan -O: enable OS detection -n: do not do DNS resolution -oA: output in the three major formats (nmap, gnmap, xml) at once # nmap -v -sS -O -n target -oA output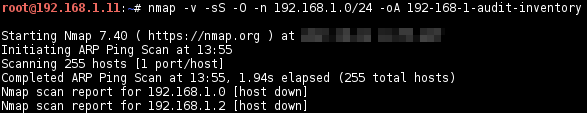
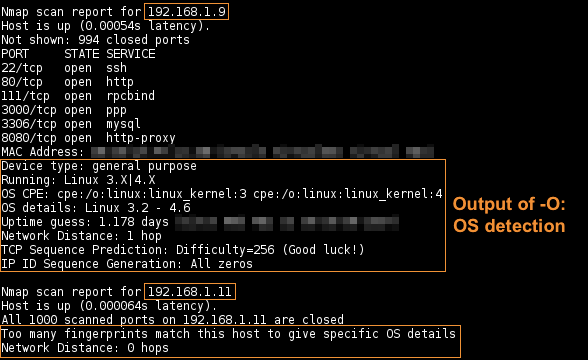

- Completed TCP SYN scan (
-sS) on in approx. - The default most commong 1000 ports [1], plus OS detection for 4 hosts took approx.
- Total time is
- Completed TCP SYN scan (
Scan a Single Target
SCAN TECHNIQUES:
-sS/sT/sA/sW/sM: TCP SYN/Connect()/ACK/Window/Maimon scans
-sU: UDP Scan
-sN/sF/sX: TCP Null, FIN, and Xmas scans
--scanflags <flags>: Customize TCP scan flags
-sI <zombie host[:probeport]>: Idle scan
-sY/sZ: SCTP INIT/COOKIE-ECHO scans
-sO: IP protocol scan
-b <FTP relay host>: FTP bounce scan
-A: Aggressive scan options, equivalent to -O, -sV, -sC, --traceroute.
OS and version detection, script scanning, and traceroute.
-T<0-5>: paranoid|sneaky|polite|normal|aggressive|insane, timing template (higher is faster)
0 and 1 is slow but useful to evade IDS alerts
-O: OS detection
-sV: Probe open ports to determine service/version info
# nmap -A -T4 target
# nmap -sS -O -sV -T4 target
# nmap -p 1-65535 -sS -sV -T4 target <- full TCP port scan
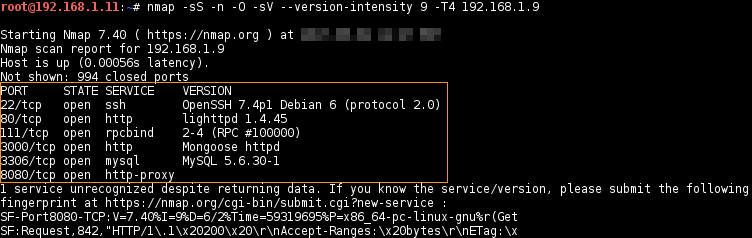
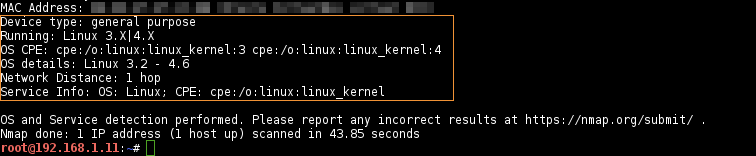
Remote OS and Service Detection
# nmap -sS -n -O -sV --version-intensity [0-9] -T[0-5] target
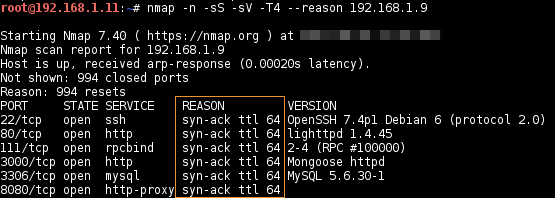
Host and Port State Reason
--reason (Host and port state reasons)
Display the reason a port is in a particular state:
For e.g., a RST packet from a closed port or an echo reply from an alive host.
List of Examples
A full-scan to see whether the which ports/packets can pass through the firewall unfiltered:
-sA: TCP ACK scan, to map out firewall rulesets: stateful or not and which ports are filtered.
-f: fragmet packets, splits the packets into 8 bytes or less after the IP header.
A 20-byte TCP header would be split into 3 packets. 2 with 8 bytes of the TCP header,
and 1 with the final 4.
Specify -ff to use 16 bytes per fragment (reducing the number of fragments).
The purpose is to make it harder for packet filters, IDS.
-r: do not randomize port, scan in numerical order
# nmap -v -p 1-65535 -sA -ff -r -n 192.168.1.1/24
Scan the network for suspicious malware infected open ports:
-PE: ICMP Echo <- ICMP ping echo (host discovery)
-sS: TCP SYN Scan
-sU: UDP Scan
-p U:2140,T:2745 <- UDP port 2140, TCP port 2745
# nmap -PE -sS -sU -sV -p U:2140,T:2745 172.16.0.0/12
References: